What is Microbial Analysis?
Microbial Analysis
The microbial analysis is the study of bacteria and other microorganisms in food. The process involves the detection of metabolites and identifying specific types of organisms. The results of food microbiology do not provide a specific count of the microbial populations present. It is essential to understand that microbial analysis can provide accurate information on the number of pathogenic organisms present in a sample.
Why is it Important?
Various industries worldwide rely on microbial analysis to detect contaminants. As well as maintain quality standards. Microbial tests are used to determine the presence or absence of a particular organism.
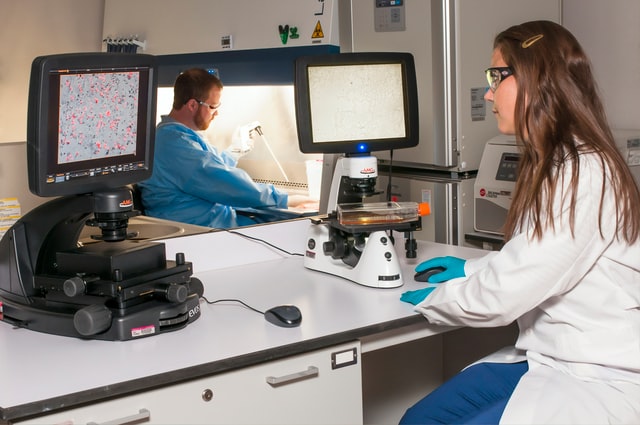

Do many industries aim to understand what is the goal of microbiological testing? The microbial analysis aims to identify organisms in culture media using a microscope. The minimum sensitivity of these tests is essential.
This is because it helps microbiologists distinguish what is a microbe in the sample. They also help determine whether a new material, method, or environment is better than the one used previously.
The test results for both the control and the main experiment must be done simultaneously. And in the same place. In some cases, a sample from a natural environment may also be tested for its contamination levels.
The 3 Common Analytic Tests
The samples should be tested using standardized procedures for a successful microbiological analysis. The three standard microbial analytic tests carried out are:
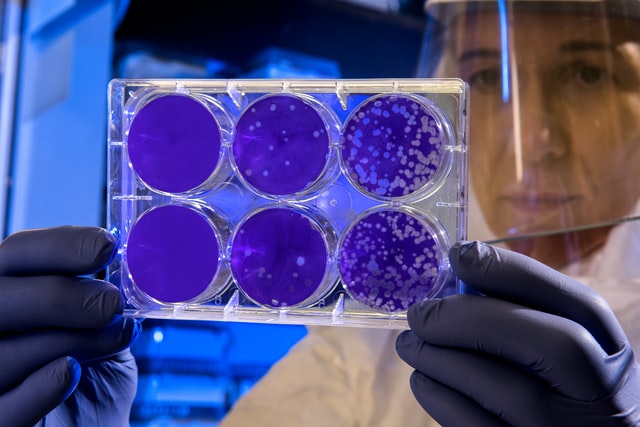
Culture Media
Culture media, also known as growth media, is a particular combination of nutrients and other chemicals. These help microorganisms like bacteria and fungi grow (yeasts and molds). Culture media is used for quality control tests of nonsterile raw materials and finished products and sterility tests, such as hygiene monitoring, sterilization process validation, and determining the effectiveness of preservatives and antimicrobial agents. Various types of cultural media are available for different purposes.
The process for performing the test depends on the sample volume, incubation time, and temperature. While many tests require a warm incubator, small-volume tests can be heated by body heat.
Immunoassay
An immunoassay is a biochemical test that uses an antibody or an antigen to determine the presence or concentration. Or a small molecule in a solution. Some immunoassays can be performed simply by mixing the reagents and samples. It is then measuring the results.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The PCR method is a powerful tool for microbial diagnostics. It includes viral and parasitic detection, quantification, and typing. Polymerase chain reaction tests detect specific genes and alleles of microorganisms.
These tests have been adapted for routine microbial diagnostics. And some laboratories have even replaced artistic techniques altogether. But, any PRC should be validated by a microbiology services laboratory before it can be used for microbial research.
The results
Depending on the application, the results of a microbial analysis are used to ensure that the product is safe for consumption. It can be used to detect bacteria. Or other microorganisms that cause diseases. As well as identify products that have shortened shelf lives or are harmful to the consumer. Using a microbial analysis, manufacturers can avoid any potential problems associated with the contaminated product.
